Where and for what is heat shrink tubing, also known as heat shrink sleeves, used?
Heat shrink tubing is mainly used in electronics and electrical engineering, usually as electrical insulation. Heat shrink sleeves are also used for mechanical protection, especially of wires and cables, as well as for protection against chemical and atmospheric factors. Moreover, they are also employed in cable marking systems, both for simple colour coding as well as for the production of printable heat shrink markers for use in thermal transfer printers.
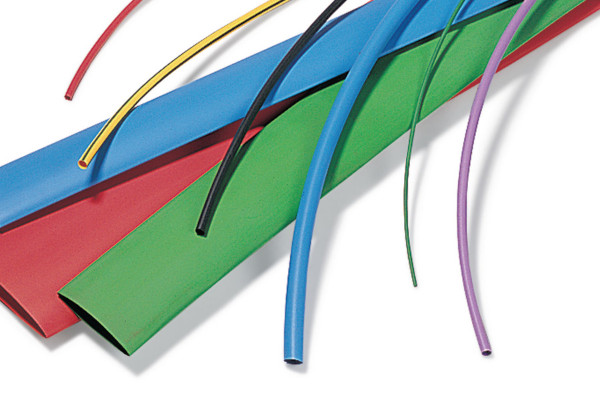
Thin-walled heat shrink tubing
Heat shrink tubing is produced by extrusion as ordinary insulating tubes of a specific diameter. Such tubes are then exposed to ionising radiation, which results in polymerisation, i.e. cross-linking. In this way, the material acquires a so-called shape memory. It is only the cross-linked tubing that is stretched to the diameter supplied, i.e. the diameter before shrinking. The diameter after maximum shrinking of the heat shrink tubing is equal to the nominal diameter of the extruded insulating tube at the start of the production process. For this reason, heat shrink tubing is usually marked with numbers indicating the diameter before shrinking (supplied diameter) and the diameter after maximum shrinking (recovered diameter), in addition to the type designation.
Standard thin-walled heat shrink tubing
Thin-walled heat shrink tubing can be made from various materials. In the past, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) was often used for the production of heat-shrinkable tubing, but nowadays polyolefins, which are derivatives of polyethylene, are used due to their much better properties. Polyolefin heat shrink tubing is characterised by its high flexibility, a wide range of operating temperatures and higher transparency (transparent heat shrink tubing).

Premium thin-walled heat shrink tubing
Depending on the quality of the material, we can distinguish between standard heat shrink tubing and premium heat shrink tubing. Although they appear to be the same material, differences can be found in the mechanical parameters (such as flexibility) or electrical parameters (such as electrical breakdown strength). In addition, premium heat shrink tubing usually has more different certifications and approvals, e.g. UL, UL224 VW-1, CSA, JAR/FAR 25.853, NF F 00-608, SAE-AMS-DTL23053. This is why premium heat shrink tubing is used in more demanding applications, e.g. in the electronics industry or where standard flexibility or standard parameters are insufficient.
Adhesive-lined thin-walled heat shrink tubing
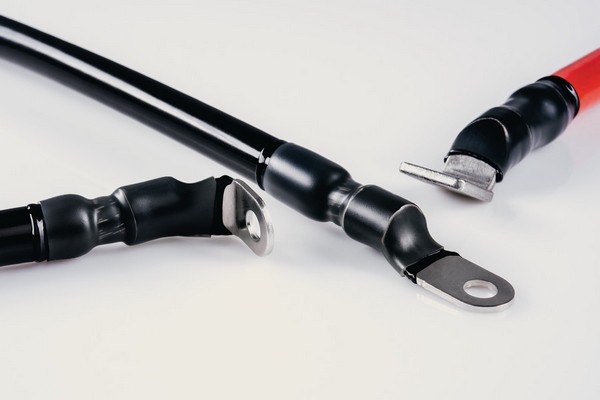
Thin-walled heat shrink tubing with adhesive lining is made identically to standard heat shrink tubing, only after being stretched to the supplied diameter, it is coated on the inside with hot melt adhesive. When the heat shrink tubing is being shrunk, under the influence of high temperatures, the adhesive changes to a liquid phase and fills the gap between the heat shrink tubing and the component on which it is being shrunk. This prevents moisture from penetrating between the heat shrink tubing and for example the outer sheath of the cable (the so-called capillary effect) and also ensures that the heat shrink tubing is securely fixed to the object.


Thick-walled heat shrink tubing
While thin-walled heat shrink tubing usually has a wall thickness after maximum shrinking of less than 1 mm, thick-walled heat shrink tubing has a wall thickness at a maximum shrink of up to several millimetres. For this reason, thick-walled heat shrink tubing is much stiffer than thin-walled shrink tubing (despite the same material) and is therefore usually supplied in 1 m lengths. Heat shrink tubing with this wall thickness provides both greater mechanical resistance and higher dielectric strength.
Depending on the wall thickness, thick-walled heat shrink tubing can be divided into medium-walled tubing (medium-walled heat shrink tubing), with a wall thickness at maximum shrinkage of approx. 2-3 mm, and thick-walled tubing (thick-walled heat shrink tubing), with a wall thickness usually greater than 3 mm. Because thick-walled heat shrink tubing has more material (thick walls) it can be stretched significantly more than thin-walled heat shrink tubing. The standard shrinkage ratio for HellermannTyton thick-walled heat shrink tubing offered by our company is 4:1 and 6:1.
Adhesive-lined thick-walled heat shrink tubing
Similar to thin-walled heat shrink tubing, thick-walled heat shrink tubing can be lined on the inside with hot-melt adhesive. This is particularly useful when greater dielectric and mechanical strength is required and at the same time resistance to moisture ingress. Such requirements are most often found in the energy sector. This is why thick-walled heat shrink tubing with adhesive lining is most commonly used in this sector.

Polyolefin heat shrink tubing
Polyolefin heat shrink tubing can be characterised as being designed for special applications, for example in the defence and aerospace industries. This type of heat shrink tubing also has special certificates and approvals according to LEA, MIL-DTL-23053, DEF STAN 59-97, NF F 00-608, NSA937211, PAN6493, SAE-AMS-DTL23053, VG95343. Among these speciality heat shrink tubing is HellermannTyton's TR27 halogen-free heat shrink tubing, which is primarily designed for use in railway applications. This is confirmed by the EN45545-2 certificate.
Heat shrink tubing resistant to diesel fuel
In addition to polyolefin, heat shrink tubing can be made from other specialised materials that offer special properties. One of these materials is cross-linked elastomer. HellermannTyton's SE28 heat shrink tubing is designed for long-term protection of wiring harnesses in military equipment, motorsport and aviation.


Heat shrink tubing resistant to high temperatures and aggressive chemicals
Other materials used to manufacture heat shrinkable tubing are polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF (commonly known as Kynar®), cross-linked fluoropolymer FPMX (so-called VITON®) and polytetrafluoroethylene PTFE (Teflon®). All heat shrink tubing made from these materials is characterised by high temperature resistance (from -70°C to +260°C) and excellent resistance to aggressive chemicals. This type of heat shrink tubing is typically used in the defence, aerospace, chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Special adhesive-lined heat shrink tubing
Similar to standard heat shrink tubing, special heat shrink tubing comes with an adhesive lining. These are usually polyolefin heat shrink tubing for the automotive, rail, defence or aerospace industries.
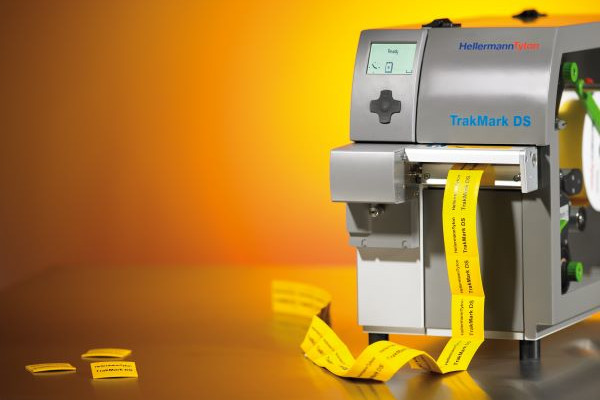


Printable heat shrink tubing supplied as a continuous tube
A special group of heat shrink tubing is heat shrink tubing for marking. A thermal transfer printer is used to print the markings onto the heat shrink tubing. The heat shrink tubing for printing is flattened and the surface is appropriately prepared so that the print is legible and durable and the thermal transfer printer does not suffer from excessive wear. Continuous heat shrink tubing for printing is usually supplied on small rolls that fit inside the thermal transfer printer.
Our product range includes standard and special printable heat shrink tubing, e.g. halogen-free, diesel-resistant and heat-resistant. The heat shrink tubing for printing also has the relevant certificates and approvals required for military, aerospace and rail applications.
Printable ladder-style heat shrink markers
In addition to printable continuous heat shrink tubing, printable ladder-style heat shrink markers are also available. These are heat shrink tubing cut into 50 mm lengths and applied to the carrier tape. This creates a ladder of heat shrink markers. This method of feeding the heat shrink tubing into the thermal transfer printer is more convenient and makes it easier to install the markers later on. Heat shrink tubing in 50mm lengths can be perforated once in the centre to produce two 25mm heat shrinkable markers or twice at equal intervals to produce three 16mm heat shrink markers.


Heat shrink moulded shapes for military applications
Completely different heat shrinkable products than heat shrink tubing are heat shrink moulded shapes. These are components which take on a specific shape after shrinking. The production process of heat shrinkable moulded shapes therefore differs from that of heat shrink tubing. Due to the unevenness of the shape, polymerisation by radiation cannot be used. For this reason, a special granulate formula is used, which, at the time of forming the moulded shape by injection moulding, chemically polymerises providing the heat shrink moulded shape with shape memory. The moulded shape after being heated is then mechanically stretched to the size supplied.
Heat shrink moulded shapes can be made from various materials to suit different applications. Heat shrink moulded shapes (also known as boots) are mostly used in the military sector to electrically protect connectors but also to prevent wires from being pulled out of the connector. They are also used to separate the cables of the cable harness. Heat shrink moulded shapes in combination with the appropriate heat shrink tubing are used to create military electrical harnesses.
Heat shrink moulded shapes for energy applications
Less demanding materials are used to manufacture heat shrinkable moulded shapes for energy applications. The most commonly used are so-called heat shrink breakout boots used to split single wires out of a cable branch and heat shrink end caps fitted to the ends of cables to protect them against moisture. For these purposes, moulded shapes are supplied with an adhesive layer.
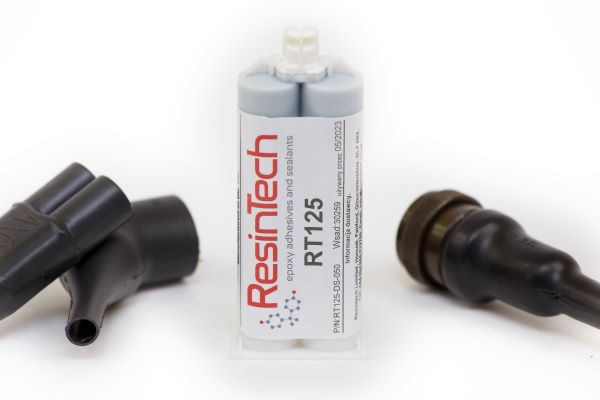
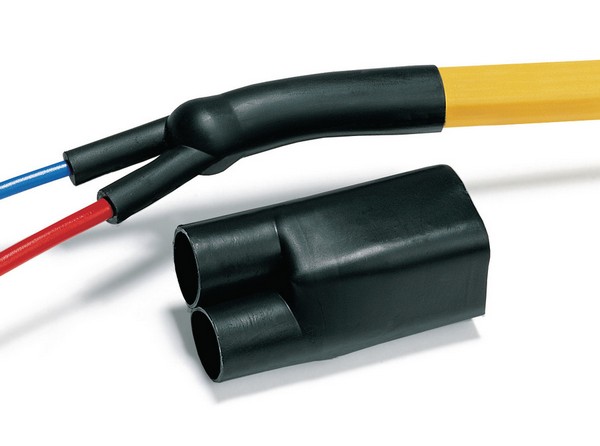

Adhesive for heat shrink tubing and moulded shapes
Sometimes the thin layer of adhesive with which heat shrink tubing and heat shrink moulded shapes are lined is insufficient. For this reason, additional hot melt adhesive in the form of tape or a two-component epoxy adhesive is used to seal the gap between the heat shrink tubing and the component on which the heat shrink tubing is applied. Heat shrink tubing and heat shrinkable moulded shapes that are not lined with adhesive can also be sealed using adhesives for heat shrink tubing.

